<br />
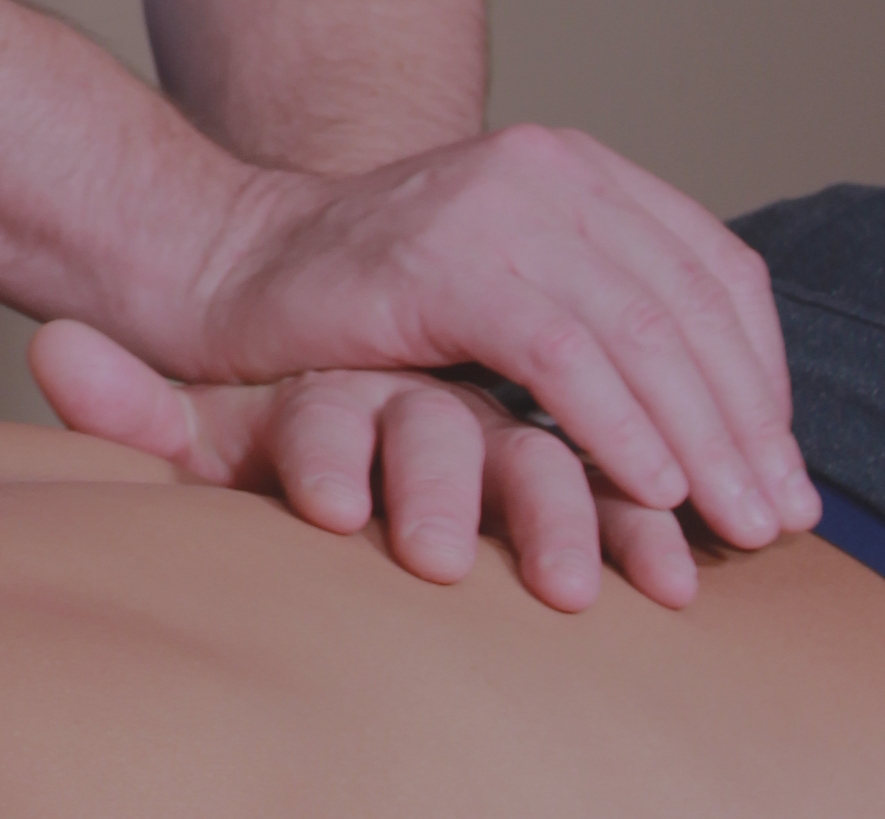
Diploma in Osteopathic Manual Practice
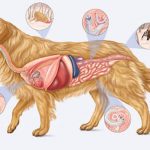
The Diploma in Osteopathic Manual Practice (DOMP) program is aimed at health practitioners keen on a career in manual osteopathy.
$4,900.00

Associate Certificate in Osteopathy in association with NTC/ICOM
The Associate Certificate in Osteopathy is intended for wellness professionals keen on expanding their practice into the field of Osteopathy.
$499.00